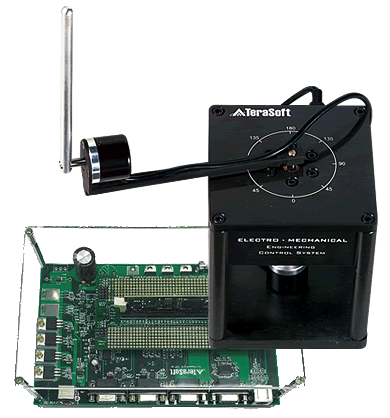
ELECTRO-MECHANICAL Engineering Control System (EMECS)
Function

1.Swing up and balancing control of rotary inverted pendulum
A laboratory exercise is to configure EMECS as a rotary inverted pendulum. The rotary inverted pendulum is a highly nonlinear system. The control purpose of this experiment is to design a hybrid controller for swing up and balancing control of the pendulum in the vertical-upright position.

2.Swing up and balancing control of arm-driven inverted pendulum
An arm-driven inverted pendulum is a two-link robot arm where both links can rotate freely in the vertical plane but only one is actuated. The objective of this experiment is to design swing up and balancing controllers for two different unstable equilibrium configurations.

3.Position Control
EMECS can be configured to control a DC servo motor with an attached inertial load. A position control system is designed such that the output angle tracks a commanded position.
-
4.Speed Control Mode
EMECS can be configured to control the speed of a DC servo motor. The configuration is the same as that of position control above. A feedback controller is designed to regulate the speed of the output shaft and reduce the closed-loop steady state error.
-
5.Haptic Control
The objective of this experiment is to establish the detent-action models for haptic control. Two Simulink models are provided and implemented on the servo motor module with the inertial load disc. The inertial load disc serves as a haptic knob. By turning the haptic knob, the user can feel the effects of the force-feedback of haptic detents.
